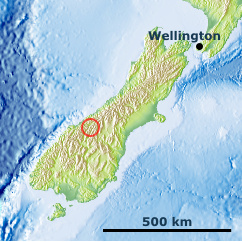
New Zealand Alps, S-Island
The highest mountains of New Zealand are found in the N-S cordillera of the South Island, the so-called New Zealand Alps, with Mt. Cook reaching 3754 m. The western flanks are very wet, receiving several meters of rainfall per year in the south. The E-flanks are drier, but there is no drought at alpine elevations. Very attractive alpine vegetation is also found in the Old Man and Rock and Pillar Ranges of Otago. The treeline is formed by Nothofagus sp. at 1200 m elevation.
4 -
Shrubs of
Hebe poppelwellii
(Scrophulariaceae) at 1300 m in the Rock and Pillar Range - one of the many
Hebe
species.
5 -
Aciphylla hektori
(Apiaceae) - male and female inflorescence.
Aciphylla
is a genus with many species in New Zealand.
6 -
Lobelia linnaeoides
(Campanulaceae). Compare the giant rosettes in the marshes of
central Africa
and a similarly small species of this genus in
Venezuela.
9 -
Snow tussock grasses (one of the three
Chionochloa
(Poaceae) species) at 1550 m on Mt. Brewster. Note the similar appearance of
Carex curvula
(Cyperaceae) in the
Alps.